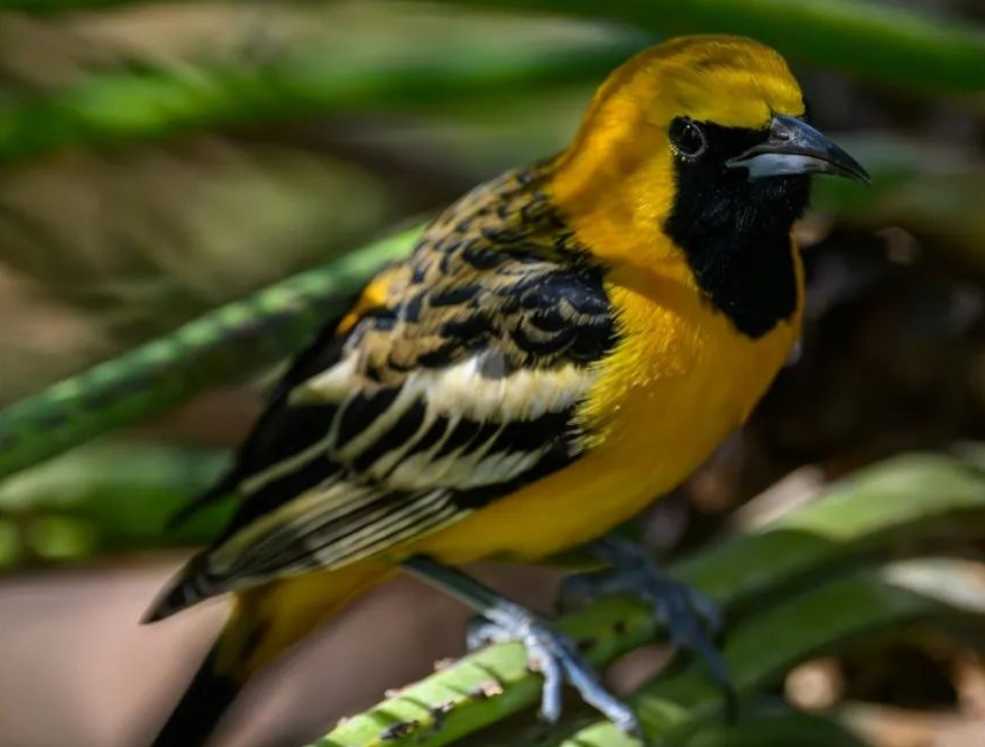
Native to the southwestern United States and parts of Mexico, hooded orioles favor riparian woodlands, orchards, and suburban gardens. They are known for their acrobatic foraging behavior, skillfully hanging upside - down from branches to extract nectar from flowers using their slender, curved bills. They also consume insects, spiders, and fruits, playing a vital role in controlling pest populations and aiding in pollination and seed dispersal. During breeding, females construct elaborate, hanging basket - like nests from plant fibers, suspended from the tips of branches.
Despite their adaptability, hooded orioles face growing threats. Habitat loss due to urban development and deforestation, as well as the impacts of climate change on their food sources and nesting sites, endanger their populations. Conservation initiatives focusing on habitat restoration, creating bird - friendly landscapes, and raising public awareness about these captivating birds are crucial to ensure their survival and continued presence in the wild.